Meteorological satellites are a type of artificial satellite used primarily to observe the weather and climate on Earth. Meteorological satellites not only observe clouds and cloud systems. Satellite images of the city can be observed in the city, fire, pollution, aurora, sand and sand storms, snow covered areas, ice maps, ocean currents, wasteful energy … and other environmental information collected by meteorological satellites.
History of the formation of meteorological satellites
The first meteorological satellite, Vanguard 2 remote sensing satellite, was launched on February 17, 1959. It was designed to measure cloud cover. However, because the axis of rotation is incorrect, it does not collect much useful data.
The first successful meteorological satellite was TIROS-1, launched by NASA on April 1, 1960. TIROS operated for 78 days and proved to be far more successful than the open Vanguard 2. TIROS Road for more advanced meteorological satellites in the future.
Types of meteorological satellite images
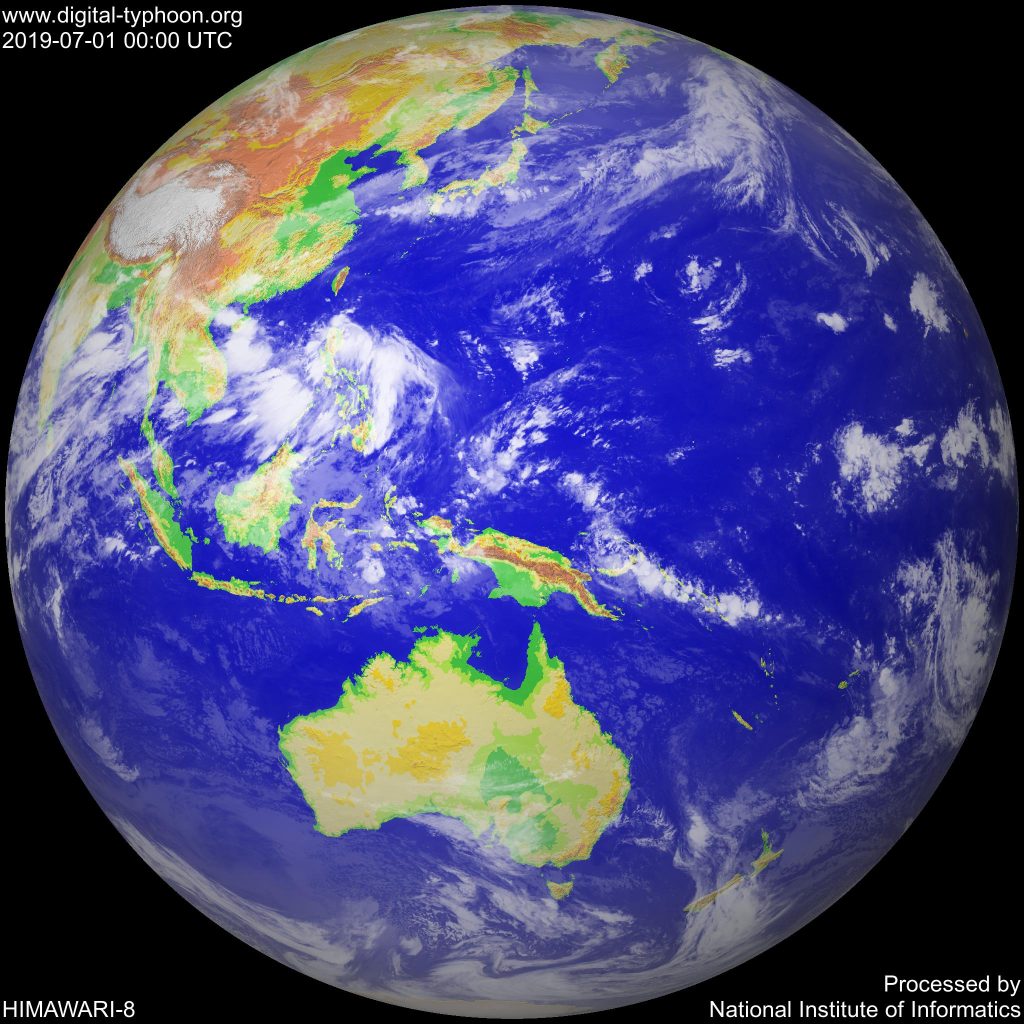
Meteorological satellites often have two basic orbits: geostationary orbits (geostationary satellites) and polar orbits.
Geostatic meteorological satellites circulate the Earth above the equator at an altitude of about 35,880 km (22,300 miles). In this orbit, the satellites are facing the same direction as the Earth, so it has a fixed position compared to the ground.
Therefore, it can transmit images of the lower hemisphere continuously with its cameras and infrared sensors. News agencies report weather information using images from remote sensing stations in weather forecast programs such as photos or put together into animations to show weather changes.
The geostationary meteorological satellite is active
- The United States, meteorological satellites GOES-9, GOES-10, and GOES-12. GOES-12 is dubbed the GOES-East, located above the Amazon River and provides most of the US weather information.
- GOES-10 is also known as GOES-West located on the Eastern Pacific Ocean.
- Europe has Meteosat-6, Meteosat-7 and Meteosat-8 satellites flying across the Atlantic and Meteosat-5 flying over the Indian Ocean.
- Russia has a GOMS satellite flying over the southern equator of Moscow.
- India also has geostationary satellites containing weather equipment.
- China has a Phong Van satellite.
Orbital satellites orbiting the Earth
- Polar-orbiting satellites circumnavigate the Earth at an altitude of 720 to 800 km (about 450 to 500 miles) from north to south or vice versa and pass through the poles along the way.
- Polar-orbiting satellites have a solar orbit, which means it can observe any position on the earth and twice a day with the same light conditions because the local time where it passes is almost constant.
- The United States has NOAA satellites that are polar orbit satellites, currently NOAA 12, NOAA 14 are reserved, NOAA 15 and NOAA 16 are submarines, NOAA 17 and NOAA 18 are main vessels.
- Russia has satellite METEOR and RESURS.
- China and India also have polar-orbiting satellites.

Satellite image is taken from remote sensing image
The Operation process of meteorological satellites in the weather forecast
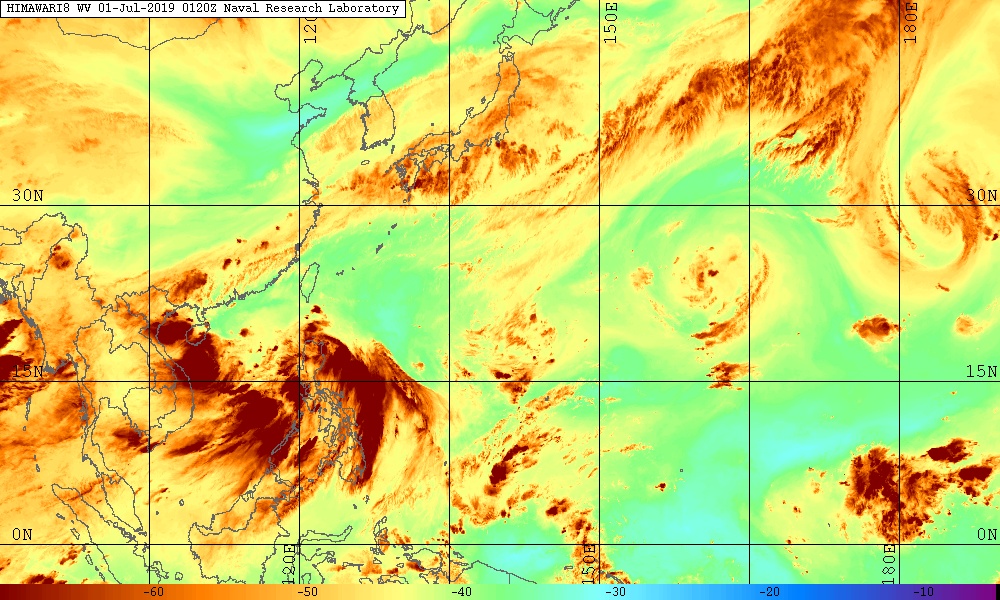
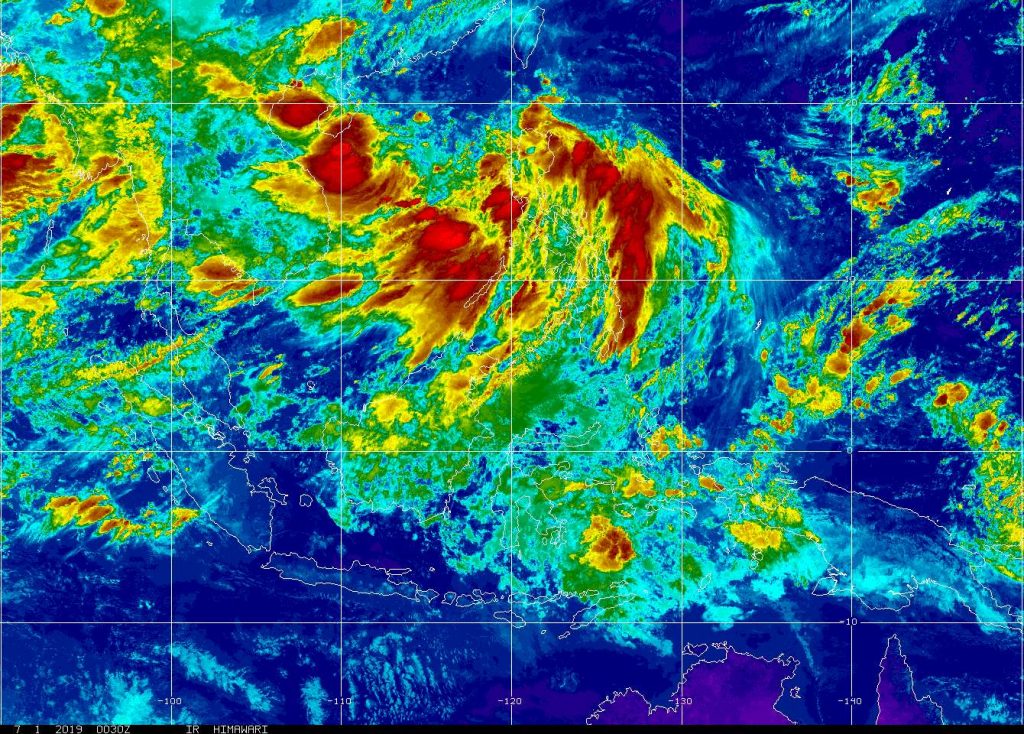
Images taken from meteorological satellites in the daytime with the naked eye can still be understood; clouds, clouds such as tropical storms, lakes, forests, mountains, snow, fire, pollution, smoke, fog … all appear. Even wind can still be determined based on cloud shape, arrangement and movement from previous images.
Infrared image meteorological satellite
Infrared images of remote sensing satellites describe sea whirlpools and maps of valuable maritime and industrial ocean currents.
Fishermen and farmers also need to know the temperature of the ground and water surface to protect crops from freezing or increasing catches at sea. El Niño phenomenon can also be determined.
Using the technique of coloring digital photos, the shades of gray are transformed into colors to determine the desired information easily.
Process of processing and analyzing remote sensing image data
Thermal imaging with sensors
Temperature shots taken with sensors allow analysts to determine altitude and cloud type, calculate ground and water temperatures, set sea surface points.
Provide satellite image cloud
- Provide weather cloud images of regions across the country
- Provide monitoring data on military and civil airports across the country
- Provides high and low floor wind maps across the region
- Provide a system of satellite cloud images across the region
Vietnam Weather, providing satellite cloud images forecast areas of Cucon and May Cb clouds, dangerous weather areas with cloudy clouds.
Source: Wikipedia, thoitietvietnam
Ngoc Hien